




/tpg%2Fe2b7a5c4-d0eb-4e48-aaff-e2047943b074.jpeg)




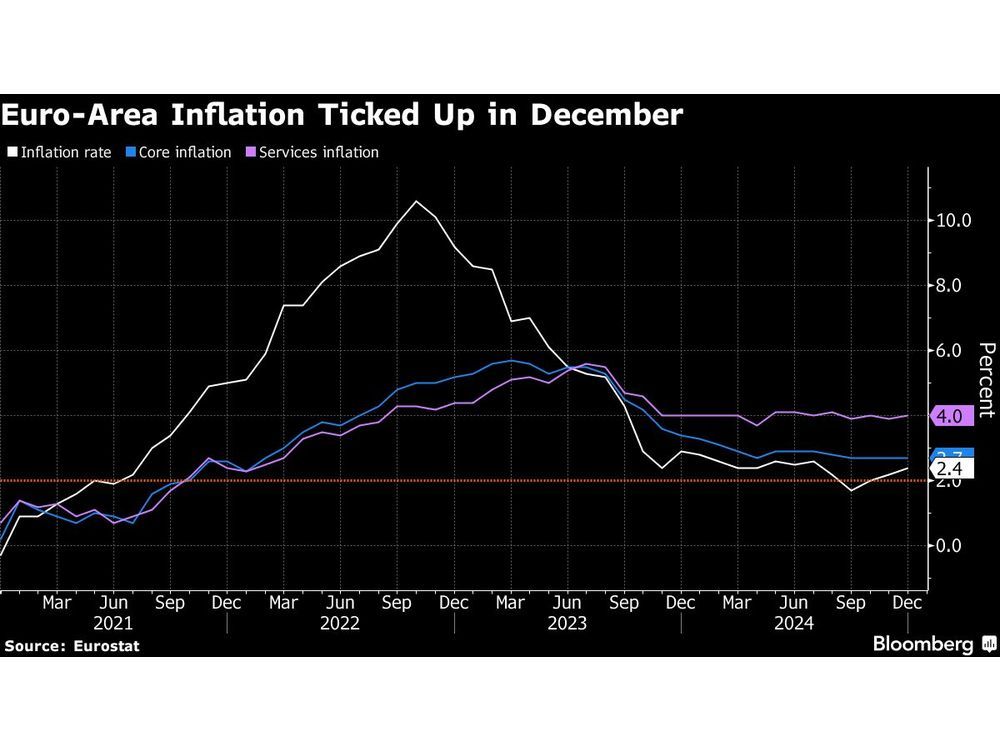



On February 3, 2025, the European Central Bank (ECB) cut its key deposit rate from 3.00% to 2.75%, alongside reductions in the main refinancing rate from 3.15% to 2.90% and the marginal lending rate from 3.40% to 3.15%. This decision, announced on January 30, 2025, marks the fifth consecutive reduction since June 2024, aiming to stimulate the eurozone's struggling economy, which recorded zero growth in the final quarter of 2024. ECB President Christine Lagarde expressed optimism regarding disinflation, stating that inflation is expected to fall to the bank's target of 2% within the year, despite the current rate standing at 2.5%, up from 2.4% in December 2024 [5496202c][742f950e].
The eurozone's GDP grew only 0.7% in 2024, with Germany's economy contracting by 0.2% for the second consecutive year and France experiencing a slight decline of 0.1%. In contrast, Portugal saw a growth of 1.5% [44797558][742f950e]. Political turmoil in Germany, with a national election scheduled for February 23, 2025, and a divided Parliament in France, is contributing to economic uncertainty, delaying potential reforms [44797558]. Lagarde emphasized the importance of economic reforms and enhancing competitiveness within the eurozone, especially considering the region's trade surplus with the U.S. was nearly 1% of GDP in 2023 [287374bf]. Recent data indicates that the eurozone GDP was flat at 0% growth in Q4 2024, following a 0.4% growth in Q3 [66ea35e7].
The recent uptick in inflation has been attributed to rising energy costs, which increased by 1.8% year-on-year in January 2025, and regional variations, particularly in Spain, where inflation accelerated to 2.8% in December 2024 [2b605308][742f950e]. Core inflation remained stable at 2.7%, while services sector inflation slowed to 3.9% [742f950e]. Bank of France Governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau has expressed vigilance regarding inflation but remains unconcerned about immediate threats, suggesting that the ECB's monetary loosening plans are intact [e8e55f8b].
Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve has maintained its interest rates at 4.25%-4.50% amid a solid U.S. economy, which saw a robust growth of 4.2% in household spending at the end of 2024 [bb505a5f]. The Federal Reserve's decision to hold rates comes as it awaits more data on inflation, while the ECB continues its path of rate cuts to address economic stagnation in the eurozone [bb505a5f][32259fa3].
The Federal Reserve's preferred inflation measure, the PCE price index, is expected to show a 2.6% increase year-on-year for December 2024, up from 2.4% in November, while Core PCE is forecasted to remain at 2.8% [32259fa3]. However, the potential impact of U.S. trade policies under President Donald Trump looms large. Trump has criticized the European Union, calling it “very, very bad” for U.S. trade, raising concerns about how tariffs could affect the euro-area economy [e8e55f8b]. Spanish central-bank chief Jose Luis Escriva has highlighted the uncertainty surrounding the impacts of these tariffs, which could complicate the ECB's monetary policy decisions [e8e55f8b].
Philip Lane, the ECB's chief economist, has previously noted that exchange rates significantly influence the euro-area economy over time, and substantial euro-dollar movements could affect prices in Europe [cefade41]. Analysts predict further quarter-point cuts in March, with expectations to reach a 2% rate by year-end, but uncertainty looms regarding future decisions due to differing views among ECB members [66ea35e7][303b0087]. The ECB aims to reach a neutral interest rate of 1.75%-2.25%, which will be critical in navigating the challenges posed by both domestic inflationary pressures and external economic factors [e8e55f8b].
As of February 5, 2025, the ECB has officially implemented a 0.25% cut to the deposit rate, marking the fifth rate cut since summer 2024. Analysts expect additional cuts, potentially lowering rates below 2.5% by the end of 2025 [43f66999]. In parallel, the Federal Reserve has paused interest rate cuts after three consecutive reductions in 2024, holding rates at 4.25-4.50% as officials await more data on inflation. President Trump is set to impose 25% tariffs on goods from Mexico and Canada unless immigration issues are addressed, further complicating the economic landscape [8ba4ce93][32259fa3]. The U.S. trade deficit in goods jumped 18% to $122.1 billion in December 2024, highlighting the impact of trade policies on the economy [8ba4ce93].
As the ECB prepares for its upcoming meeting on March 6, 2025, the interplay between inflation trends, exchange rates, and Trump's economic policies will be crucial in shaping its approach to stabilizing the eurozone economy [c152e519]. Lagarde's emphasis on the need for reforms and competitiveness underscores the urgency of addressing these external pressures as part of the ECB's broader strategy [287374bf].