




The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on various industries, including personal injury law, insurance claims, risk management, and corporate criminal liability, is a topic of ongoing discussion. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perceive, reason, learn, and solve problems. In personal injury law, AI has transformed practices and provided law firms with new opportunities to reach more clients. AI techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, neural networks, data preprocessing, feature engineering, and algorithms play a crucial role in developing AI systems [ac2a8d54].
AI has streamlined various aspects of personal injury law, making processes more efficient and enabling law firms to handle complex cases. For example, AI can analyze large amounts of data, such as medical records and accident reports, to identify patterns and make predictions. This can help lawyers assess the strength of a case, determine potential damages, and provide more accurate advice to clients. AI can also assist in legal research by quickly analyzing vast amounts of legal documents and precedents to find relevant information and support legal arguments [ac2a8d54].
The use of AI in personal injury law is not limited to data analysis and research. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can interact with clients, answer frequently asked questions, and provide initial legal guidance. This can help law firms handle a larger volume of inquiries and provide timely assistance to clients. AI can also automate administrative tasks, such as document management and scheduling, freeing up lawyers' time to focus on more complex legal matters [ac2a8d54].
The impact of AI on insurance claims is also significant. Integrating AI directly into insurance claims processing improves the industry's predictive analytics capabilities and ability to apply predictive models to processing claims. AI can analyze claims trends and data, supporting informed, data-driven decisions. AI-powered predictive models using photos of damage details from claims can predict losses more accurately and consistently. With AI, the customer claimant is able to tell their story in a very intuitive and contemporary digital experience. AI automation frees up adjusters' time, allowing them to focus on complex claims or delivering better customer care [22081181].
Risk management is a crucial aspect of AI adoption in the legal and insurance industries. Lawyers and insurance professionals are exploring AI adoption and educating themselves to provide AI legal advice and address the potential risks associated with AI. Simple AI systems are already deeply integrated into society and the economy, from virtual assistants for users to anti-fraud detection for businesses. However, recent advances based on large language models are quickly increasing the pace of integration and the capacity for errors as newer AI systems replace older AI and non-AI systems. Copyright infringement, hallucinations, privacy, and bias are among the main litigation concerns regarding generative AI. Developing AI products, such as AI robots, face perils that can cause bodily injury and/or tangible property damage. The extension or limitation of existing tort law, caselaw, statutory law, and contract law with respect to AI is a question [8ae3dea2].
Insurance companies are incorporating regulatory standards in underwriting, such as the EU Artificial Intelligence Act. Lawyers can address AI perils by having a robust lawyers professional liability policy. Other insurance options include technology errors and omissions insurance, cyber liability insurance, intellectual property insurance, product/general liability insurance, employment practices liability insurance, crime insurance, and directors and officers insurance. However, there are notable gaps in coverage, lack of standardization, ambiguity in coverage scope, and the exponential nature of AI risks. Risk management should consider the frequency, severity, and velocity of evolving risk profiles. Lawyers should advise their clients to proactively address these risks through tailored insurance policies. Collaboration between stakeholders, led by legal counsel and compliance, is crucial to effectively manage and mitigate the potential perils of AI [8ae3dea2].
The challenges of policing the improper use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the context of criminal law enforcement are also being discussed. AI-driven decision-making can lead to legal violations, and questions remain on how to hold corporations criminally liable for such actions. The Department of Justice is focusing on AI and issuing policies and rules to prevent potential negative consequences of AI, such as fraud, discrimination, and data intrusions. AI is a transformative tool with great potential benefits but also carries the risk of causing tremendous damage. Regulating AI when legal violations are a result of AI-driven decision-making rather than intentional human actions presents difficulties [6d6ce6a5].
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly indispensable in various fields of penal procedure law and criminalistics. According to Dr. Csongor Herke, AI's presence in the justice system is not just a current trend but a future necessity. While there is some reluctance to fully embrace AI in the justice system, it has the potential to significantly improve processes and aid in decision-making. AI has already made its mark in the legal sector, but its use is characterized by a certain level of reservation. However, there is a strong belief that in the near future, AI could be fundamental in the formation of legal verdicts, offering enormous benefits by streamlining complex and time-consuming tasks. AI can help in predictive policing by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify patterns. However, ethical concerns such as privacy, bias, and accountability need to be taken into account when integrating AI into justice systems. It is unlikely that AI will completely replace human judgment in legal proceedings as legal judgment often involves nuances and discretion that current AI cannot replicate. Key challenges and controversies include ensuring transparency in AI systems, mitigating biases in training datasets, and balancing the benefits of AI with potential job displacement in the legal sector [4535a5b4].
The impact of AI on human rights is a pressing concern that is being explored in the Symposium on AI and Human Rights. Organized by the Promise Institute for Human Rights at UCLA School of Law, the symposium aims to delve into the complex relationship between AI and human rights. AI has the potential to both benefit and harm human rights, with implications for freedom of expression, privacy, non-discrimination, and more. The symposium will bring together experts to discuss topics such as generative AI, the impact of AI on marginalized communities, and AI governance and international law. By addressing these pressing questions, the symposium seeks to shed light on the intersection between AI and human rights [5e048e78].
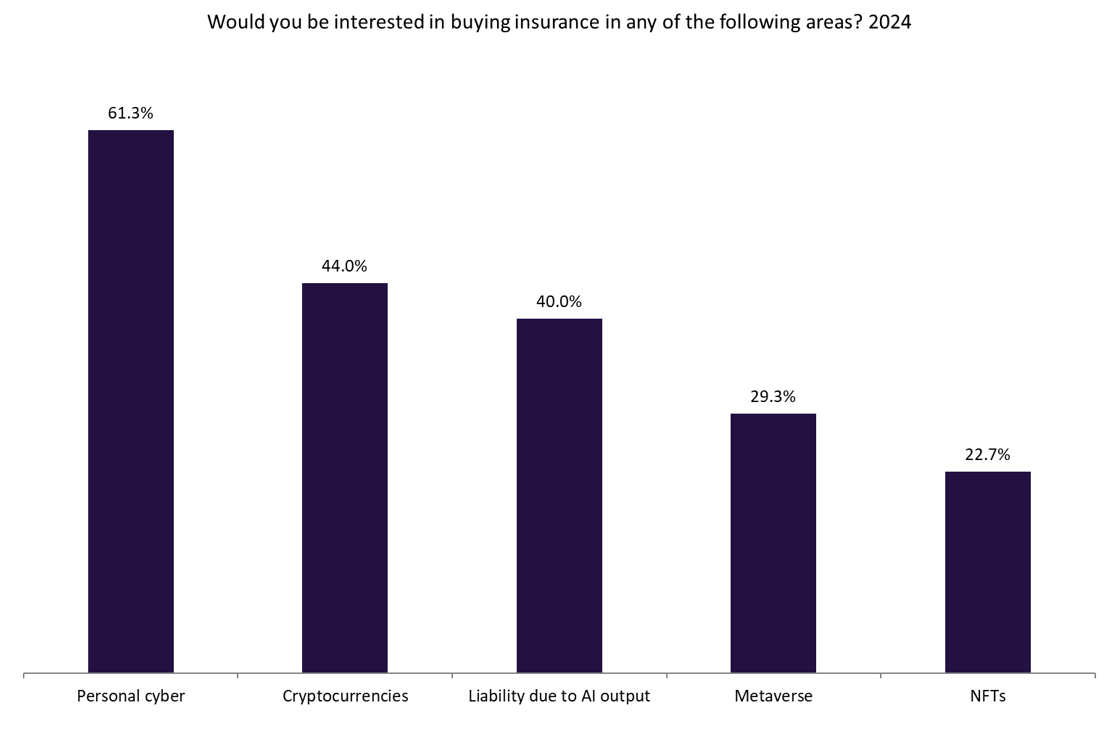
In addition to the impact of AI on various industries, there is a growing demand for insurance policies that cover the liabilities arising from dysfunctional AI outputs. A GlobalData poll revealed that 40% of respondents expressed interest in insurance policies that cover the liabilities resulting from dysfunctional AI outputs. This highlights the recognition of the potential risks associated with AI and the need for risk management strategies to mitigate these risks [513f0552].
Orbital Witness and First Title Insurance have already launched an insurance policy that covers the accuracy of generative AI outputs. This policy offers protection against errors in AI-driven processes, particularly for real estate transactions. Inaccurate AI outputs can lead to significant monetary losses, lawsuits, regulatory penalties, damage to reputation, and operational disruptions. Insurance policies that cover inaccuracies in AI outputs are crucial to mitigate these risks and are poised to become a crucial component of risk management strategies for businesses that leverage AI [513f0552].