

The ongoing debate about the impact of e-commerce on the economy has gained renewed attention, particularly in India. Union Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal recently expressed concerns regarding Amazon India's financial losses and the potential for predatory pricing strategies employed by large e-commerce platforms. He suggested that significant investments made by these giants often serve to mask losses rather than contribute positively to the Indian economy. Goyal highlighted that within the next decade, half of India's market could potentially transition to e-commerce, raising alarms about the implications for traditional retail sectors [a4437272].
In the context of global trends, Goyal pointed out the decline of traditional stores in the US and Europe, attributing this shift to the rise of e-commerce. This observation aligns with previous investigations by the US Department of Justice in 2019, which scrutinized major online platforms for issues related to market power and competition [a4437272].
Despite these concerns, some analysts, like Aarati Krishan, argue that e-commerce has significantly improved the ease of living in India, providing consumers with greater access to goods and services. This duality in perspectives reflects the complex nature of e-commerce's impact on the economy, where benefits and drawbacks coexist [a4437272].
As the World Trade Organization (WTO) continues to work on establishing global digital trade rules, the implications of e-commerce on traditional markets remain a critical point of discussion. The WTO's Joint Statement Initiative (JSI) on Electronic Commerce aims to create a framework that addresses issues such as data flows and consumer protection, although the United States has yet to join due to concerns over data privacy and protection [23a40098].
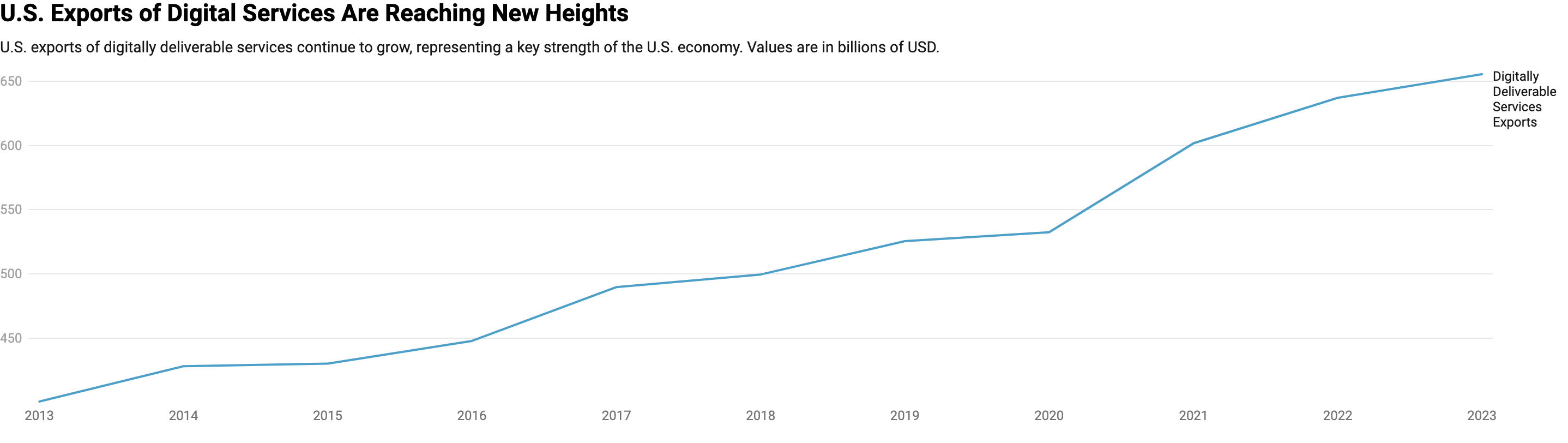
The impact of digital trade on the U.S. economy is also notable, with digitally deliverable services exports generating significant revenue. In 2023, these exports reached $655.5 billion, contributing to a trade surplus of $266.8 billion. This growth underscores the importance of digital services in the broader economic landscape [d11ee800].
As countries like Taiwan and Japan navigate their trade strategies, the competition for influence in regions like Vietnam highlights the geopolitical dimensions of e-commerce and digital trade. The U.S. and China are vying for Vietnam's partnership in supply chains, each seeking to strengthen their economic ties with the nation [0ef4c223].
In summary, while e-commerce presents opportunities for economic growth and consumer convenience, it also poses challenges for traditional retail sectors and raises questions about market fairness and sustainability. The ongoing discussions and regulatory efforts will be crucial in shaping the future landscape of e-commerce both in India and globally [a4437272].