





The trucking industry in the United States is currently navigating a complex landscape marked by both challenges and growth opportunities. As of 2023, there are over 10.77 million registered trucks in the U.S., with the industry valued at approximately $3.7 trillion globally. The trucking sector is responsible for moving about 70% of U.S. goods, accounting for 80.7% of total freight costs in the U.S. [22daef02]. Despite these impressive figures, the industry is grappling with significant challenges, including a projected shortage of 160,000 drivers by 2030 and rising concerns over the economy and fuel prices [22daef02].
Recent analysis highlights that the U.S. is facing a shortage of over 80,000 truck drivers, exacerbating the difficulties in maintaining efficient supply chains as nearshoring reshapes North American logistics [2a4fc279]. Nearshoring, which involves relocating manufacturing closer to home, offers advantages such as avoiding tariffs and reducing lead times. However, it also presents challenges, including higher domestic manufacturing costs and infrastructure constraints [2a4fc279]. As of December 2023, the trucking freight value exceeded $70 billion, with less-than-truckload (LTL) shipments accounting for 10-15% of industry volume [2a4fc279].
In recent years, the trucking sector has seen substantial job growth, adding 405,000 jobs in 2022 alone. However, driver employment has declined by 4.6% from its 2022 peak, indicating a troubling trend for the industry [a0c37a1d]. As of 2023, there are approximately 3.54 million truck drivers in the U.S., with a median salary of $45,570 [22daef02]. The industry faces headwinds as consumer spending slows and inflation continues to impact operational costs, with trucking costs increasing by 6.6% in 2023 [a0c37a1d]. The Federal diesel tax is currently set at $0.24 per gallon, which adds to the financial pressures on trucking companies [22daef02].
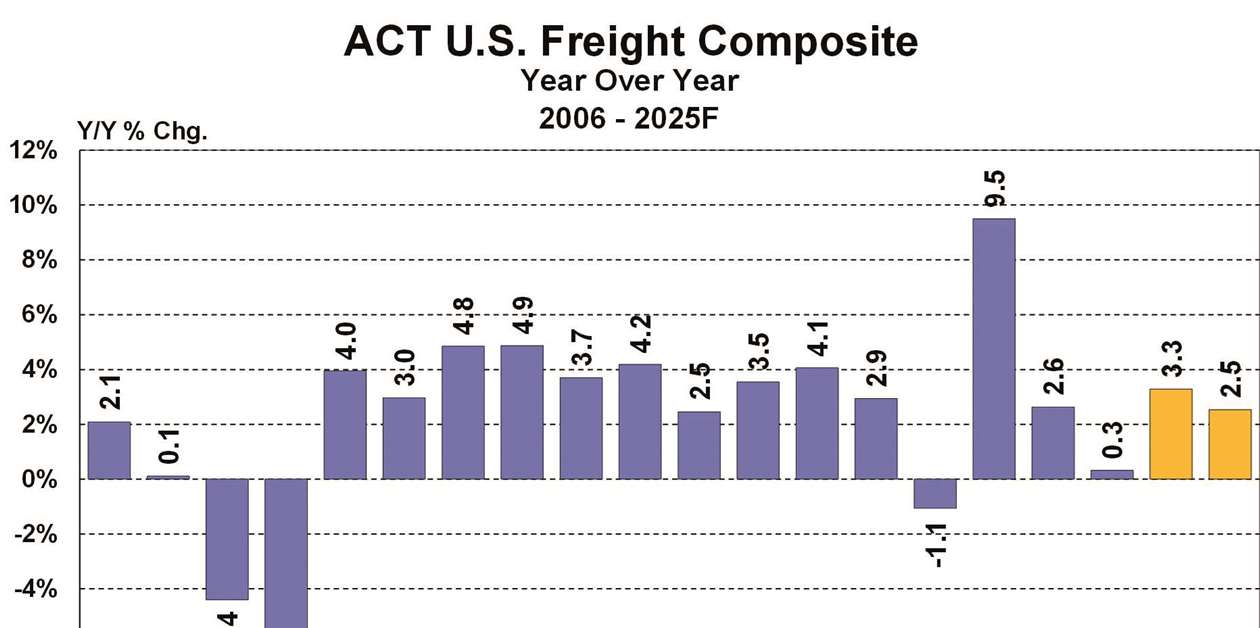
Looking ahead, the ACT Research forecasts a positive trend for the North American trucking industry, with U.S. GDP growth projected at 2.6% in Q4 2024 and 2.0% for 2025. The ACT Freight Composite Index is expected to rise by 3.2%, indicating a recovery in freight activity. However, the industry must contend with a slowdown in freight growth and economic uncertainties projected for 2025, where GDP growth is expected to drop to 2.0% year-over-year [f4779dfc][5df767f8].
The trucking industry is crucial to the U.S. economy, contributing approximately 57% of the GDP and serving as the backbone for 80% of U.S. communities that rely on trucks for goods [22daef02]. The General Freight Trucking industry alone generated $91.4 billion in revenue in 2022. Despite the challenges, the sector is expected to see a 28% growth in freight moved from 2021 to 2032, with a 9.2% growth forecasted by 2026 [22daef02].
In terms of regulatory changes, the CARB Clean Truck Regulation is pushing for fleet upgrades towards zero-emission vehicles, which may create additional challenges for trucking companies striving for rapid growth [f4779dfc]. The EPA's Clean Truck and GHG-3 regulations also face uncertainty under the new Congress, which could impact compliance costs and operational strategies for trucking firms [5df767f8]. The industry remains resilient, with high-quality operators like Old Dominion Freight Line and XPO Logistics well-positioned for recovery. Rail operators are also poised for earnings improvement, benefiting from reshoring trends [80f4879d].
Freight rates have recently increased by 7% year-over-year, reflecting the ongoing demand for transportation services [5df767f8]. However, the future of U.S. truck manufacturing is under threat due to potential policy rollbacks under the Trump administration. A recent analysis indicates that Trump's rollback of federal support for clean vehicle transitions could jeopardize $145 billion in investments and lead to the loss of over 35,000 job-years in the sector [0aa0dff5]. The loopholes in the USMCA trade agreement may allow foreign competition to undercut U.S. jobs, further complicating the landscape for domestic manufacturers [0aa0dff5].
The transition to clean vehicles is deemed essential for reducing emissions, with the 2021 Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act aimed at supporting clean vehicle manufacturing [0aa0dff5]. Without strong policies, the U.S. risks losing its competitive edge in the clean vehicle market, potentially resulting in the loss of 477,000 clean energy trucks by 2032 [0aa0dff5]. Overall, while the trucking industry faces significant challenges, including a driver shortage and rising costs, it is also on the brink of recovery and growth, driven by increasing demand for freight transportation and ongoing investments in infrastructure and technology. However, challenges in trucking are expected to limit commercial tire sales in 2025, as 9.5% of carriers exited the U.S. market from December 2022 to late 2024 [a0c37a1d].